Hazard identification and risk assessment (HIRA) is a technique to identify hazard and assess associated risk. it includes to define and implement necessary control measures to bring risk at an acceptable level. HIRA shall be regularly reviewed and updated by latest techniques.
Objectives of Hazard Identification And Risk Assessment (HIRA)
- Identify types of Hazards in workplace.
- To do risk assessment.
- Suggestion regarding control to the organization.
- Risk control implementations.
- Review and update of hazards, risk and controls.
Planning & Implementation
We can do planning and implementations of Hazard Identification and Risk Assessments by followings;
- Policy.
- Legal aspect-impact consideration.
- SOPs.
- Training to all concerns (Workmen Participation).
- Complains and Feedbacks.
- Inspections and audits (Internal and External).
- Accident and near misses investigation, review and use it in updation process.
- Performance measurement and action to be taken for improvement.
Hazard Identification
Keep workplace safe and healthy. Ensure there are no hazards for exposure to workmen. Shall look for hazards in advance to prevent potential hazards.
Actions and recommendations:
- Documented thoroughly.
- Reviewed on regular basis.
- Keen management support.
Hazard Identification Methods
- Hazard Checklists
- Surveys
- Hazard and operability study (HAZOP)
- Review
Hazard Management Process
- Identify Hazards.
- Assessment of the risk.
- Evaluation of risk.
- Control of risk by implementation.
- Monitor and review
Risk Assessment :
Evaluate risk to Environment, Health and Safety from hazards at workplace.
Three types of risk assessment.
- Qualitative – based on risk matrix , likelihood and severity (Fatality, Minor injuries, major injuries, first aid and near misses).
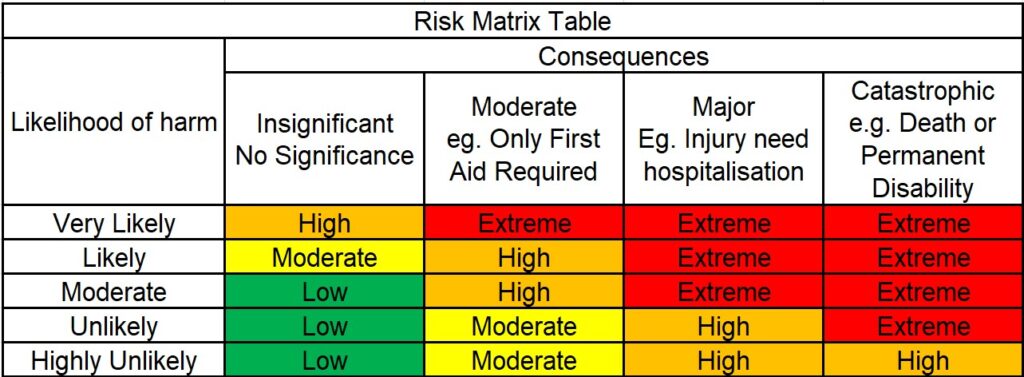
2. Semi-Quantitative
severity: First AID, Less than defined medical cases, more than defined medical case, Lead to fatality & permanent disability. Likelihood : occurrence: 1. Yearly , 2. Monthly, 3. Weekly, 4. Daily.
3. Quantitative : when there are numerous hazards, do JSA, identify and document it that can have adverse effect.
Actions and recommendations :
- Eliminate (stop work, cover hazard)
- Substitute (use substitute available)
- Isolation (temporary way to isolate)
- Engineering control (by means of permanent change in design, or any engineering/Technical Way)
- Administration Control (signage, notice, work rotation, work timing)
- Personal Protective Equipment (Helmet, mask, face shield, etc..) and Safe usage of PPE.
Risk Assessment Methods :
- What can go wrong?
- How can go wrong?
- What is the probability?
- What are the consequences?
- Who are going to be affected?
Risk Management Process:
- Activity classification (Work based, product based, services based, etc..).
- Identify hazard.
- Assess the risk.
- Risk Control.
- Review risk control.

