Key Components of Workplace Ergonomics
Let’s delve into the key elements of workplace ergonomics that fundamentally influence workmen well-being and efficiency:
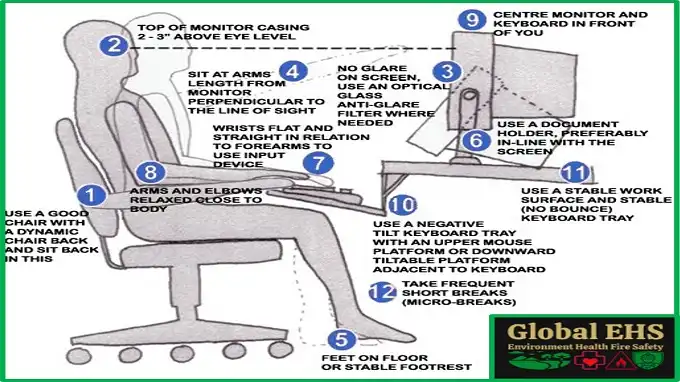
- Work area and Seat:
Choose chairs and desks that can be adjusted to fit people of all sizes and shapes. Seats support to offer lumbar help, and work areas support to consider proper keyboard and mouse placement. - Location of the Monitor:
Position screens at eye level to lessen neck strain. Utilize movable screen stands or mounts to accomplish the ideal level. - Keyboard and Mouse:
Put resources into ergonomic keyboards and mice that advance a natural wrist position. A keyboard tray can assist with keeping up with proper wrist arrangement. - Normal Breaks:
Urge workers to enjoy standard breaks to stretch and move around. This can prevent stiffness and improve circulation. - Lighting:
Guarantee proper lighting in the work area to decrease eye strain. Use task lighting to dispose of glare on screens. - Cable Management:
Keep links coordinated and far removed to prevent tripping risks and keep a perfect work area. - Ergonomic Accessories:
Provide ergonomic accessories like footrests, anti-fatigue mats, and document holders to enhance comfort and effectiveness.
Implementing Workplace Ergonomics
To harness the benefits of workplace ergonomics, consider the following steps:
- Assessment: Workstation ergonomic assessments can help you determine areas that need improvement. Encourage workers to report distress or pain.
- Training: Offer ergonomic preparation to workmen, showing them appropriate posture and how to change their work area for ideal comfort.
- Customization: Permit workmen to customize their work areas inside ergonomic rules. Perceive that everybody’s body is unique, and customization can further develop comfort.
- Feedback: Cultivate open communication among workers and management with respect to ergonomic concerns or ideas for improvement.
- Continuous Improvement: Consistently assess and adjust the work area to oblige changes in technology, tasks, or workmen necessities.

