Burns First Aid Guide
What Are Burns?
- Burns are injuries that damage and kill skin cells.
- These wounds often need special consideration and require a trip to the doctors.
- Burns can be caused from hot liquids and materials, common household chemicals, fire, radiation from the sun, and other sources.
- When someone has been burned there are three important factors that must be looked at, depth (first, second, or third degree), area (total body space covered), and location (where the burn is on the body).
- Depth is a measure of how deep the damage to the skin goes.
- We will look deeper into the three degrees of damage in the section below.
- The total body area is also important, the skin is a barrier to protect the body, and when it’s damaged, the victim is subject to fluid loss and infections.
- If more than 15% of the body surface is damaged the victim can go into shock, and may require hospitalization for IV fluid resuscitation and skin care.
- The most important factor is location.
- If a burn occurs on the neck or near the nose and mouth, the persons breathing passages may be affected.
- Burns often swell and this could become a life-threatening problem if the airways become constricted.
- Another facial burn that needs special attention are the eyes.
- These should be looked at as soon as possible and handled very seriously as burns to the eyes may lead to clouded or lost vision.
- Because burned tissues shrink, burns that extend circumferentially around body structures often require the surgical removal of the dead and damages tissue, this procedure is called an escharotomy.
- Burns are often difficult to heal and may leave scars.
Burn Prevention:
- Burns of all kinds can be prevented easily.
- Keep household chemicals out of reach of children. Make sure hazardous chemicals are well marked and caps are screwed on tight.
- Keep hot object safely out of reach and make sure to turn off heaters and stovetops when finished to prevent burns.
- Also keep socket caps over all unused electrical sockets to protect against electrical shock, and keep all electrical wires away from water.
Burn Treatment:
- Remove and constricting jewelry.
- Do NOT use oils or butter on a burn.
- Douse effected area with cool water ASAP! It can be cleansed gently with chlorhexidine solution.
- Do NOT use ice or ice-cold water, this can cause additional damage.
- If you have not received a tetanus booster within 5 years, get one to protect against tetanus infections.
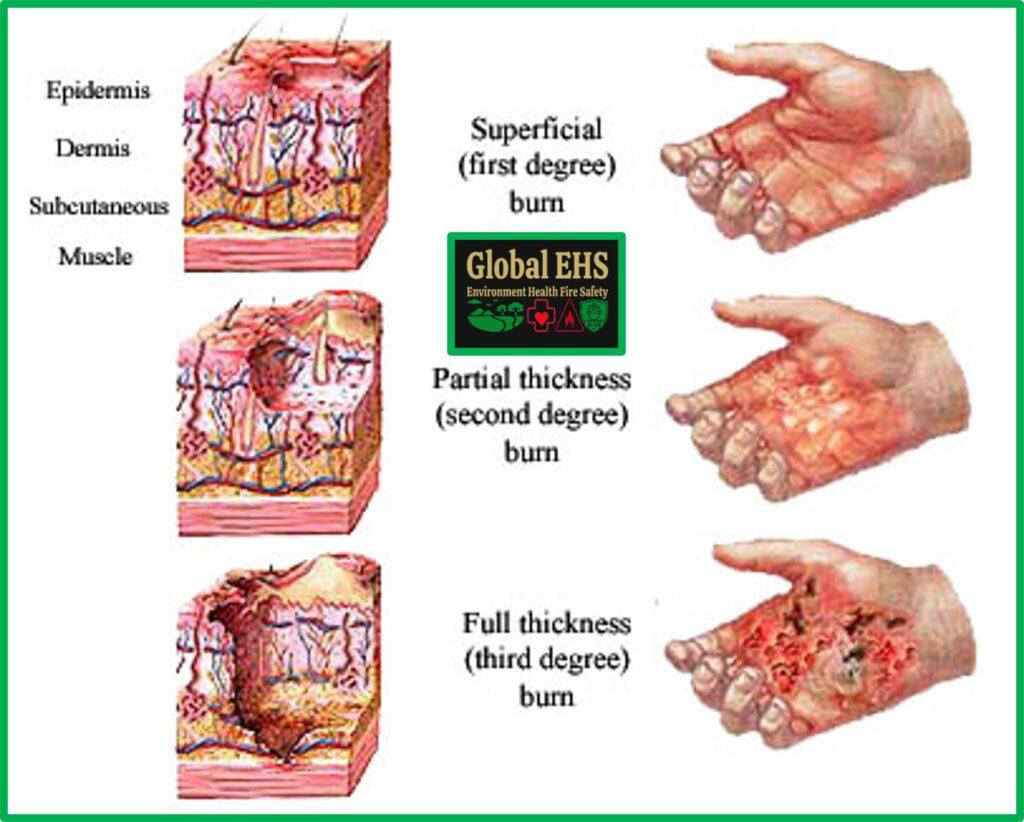
Classification and Treatment of Burns:
First Degree:
- Most first-degree burns are superficial and can be cared for at home without the help of a medical professional.
- These burns are much like typical sunburns and are cared for in a similar way.
- You should immerse the burn in cool water (do not use ice!) and then blot it gently and apply burn cream and then cover with a dry, clean, non-stick pad.
- These burns usually leave the skin red and mildly swollen.
- The skin sensations are intact and the burn is painful to the touch.
- Most average sunburns are characterized as first-degree burns.
Second Degree:
- Second degree burns are more serious and should be seen by a medical professional.
- If the burn seems very severe report to an emergency room or call Emergency number.
- Although second degree burns often look like first degree burns, in the sense that they are red, the damage goes deeper.
- With these burns, the pain is more intense and blistering may occur.
- The burns may also be wet, or weeping and may have a shiny surface.
- It is advised that these burns are not touched or covered.
Third Degree:
- These burns are the most serious. Third degree burns are very deep and the burn often appears white, deep red, or black because of skin death.
- These burns are often without sensation because nerve endings have been damaged.
- It is important that these burns are not touched, or covered unless absolutely necessary.
- Any contact with the burned skin can cause more damage and heighten the chance of infection.
Burns First Aid Treatment
For both second and third-degree burns:
- If face is affected sit the victim up and watch for breathing difficulties, until medical help is received.
- If arms and legs are affected, keep them elevated above heart level.
Burn First Aid Guide is very useful to identify degree of burns and its treatment accordingly.
Electrical Burns:
- If someone receives an electrical burn, they should seek professional attention immediately.
- These burns often result in serious muscle breakdowns, electrolyte abnormalities, and occasionally kidney failure.
- An important thing to note about these burns is that the damage is often internal and cannot be seen from the outside.
Chemical Burns:
- These burns should be treated like thermal burns and doused with large amounts of water to flush out the affected area.
- Contaminated clothing should be removed.
- It is also very important that you DO NOT try to neutralize the chemical burn by adding another chemical, as this could result in a chemical reaction causing thermal burns or greater skin damage.
- Many chemicals can be treated to reduce skin damage, so when in doubt it’s a good idea to call your local poison control center or make a trip to doctor.
- When working with chemicals always wear the proper protective gear to avoid burns and other injuries.
Burns First Aid Guide or treatment plays an vital role till medical help not arrive.
Burn First Aid Guide or treatment is very useful in case of emergency situation like fire.

