Workplace Ergonomics: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction to Workplace Ergonomics
In the quickly advancing scene of present day work, where a considerable lot of us go through hours every day at work areas or before PC screens, the idea of workplace ergonomics has acquired critical significance.
Working environment ergonomics is tied in with making a work area that fits the requirements of representatives, upgrading solace, advancing wellbeing, and eventually driving efficiency.
In this comprehensive guide, we will discuss the significant effects of ergonomics in the workplace and offer suggestions for designing ergonomic workspaces that make a difference.
Let us understand Workplace Ergonomics
Working environment ergonomics is the study of planning and organizing work areas to match the capacities and limitations of workers.
It is established in the possibility that the workplace ought to adjust to worker, not the opposite way around.
The primary goal is to reduce the risk of injury, enhance comfort, and improve overall job satisfaction.
The Connection Among Ergonomics and Worker Well-Being;
Physical Comfort and Wellbeing:
Ergonomics is as a matter of some importance about physical and mental comfort. At the point when workers are truly agreeable in their work area, they are less likely to encounter distress or pain related to musculoskeletal issues, like back pain, carpal tunnel syndrome, or eye strain.
Productivity:
A comfortable, ergonomically planned work area straightforwardly affects efficiency. Workmen can focus better on their undertakings when they are not occupied by distress or pain.
Decreased Absenteeism:
Ergonomics can reduce injuries and health issues in the workplace. This implies less days off and sick leave, at last saving time and assets for the both employees and employers.
Mental Health:
Ergonomics isn’t just about physical comfort; It also has an effect on mental health. An efficient, ergonomically planned work area can reduce stress, nervousness, and dissatisfaction.
Workplace ergonomics in manufacturing industry
In the manufacturing sector, ergonomics of the workplace play a crucial role in ensuring the health and safety of employees and increasing productivity.
In this requesting climate, where repetitive tasks, large equipment, and extended periods of time are normal, ergonomics plays a critical part in limiting the risk of injuries, upgrading efficiency, and improving overall job satisfaction.

Key aspects of ergonomic workplace design in the manufacturing sector include:
Workstation Plan:
Plan workstations with movable levels and legitimate format to accommodate different assignments and workmen heights.. This lessens strain and guarantees workmen can perform their tasks easily.
Tools and Equipment:
Give ergonomically designed tools and equipment that reduce the actual exertion expected to complete tasks. This incorporates lightweight and offset tools with comfortable holds.
Handling and lifting:
Carry out safe lifting practices and give lifting helps like derricks, transports, and forklifts to reduce risk of musculoskeletal injuries while moving heavy materials.
Seating:
In positions requiring delayed sitting, utilize ergonomic seats with lumbar help to limit the gamble of back torment. For standing undertakings, against exhaustion mats can lessen inconvenience.

Training:
Train workers in appropriate lifting methods, posture, and ergonomics attention to guarantee they understand how to safeguard themselves while performing their tasks.
Design of Machines:
Upgrade machine plan to limit repetitive movements, vibrations, and noise. This decreases the risk of repetitive strain injuries and hearing harm.
Process and Workflow Optimization:
Streamline production processes to minimize unnecessary movements and eliminate bottlenecks that can lead to worker fatigue and discomfort.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
Ensure that worker approach proper PPE, including gloves, safety goggles, and hearing protection, to protect their wellbeing.
Rotation and breaks:
Support ordinary breaks and task rotation to permit workers to rest and recover. This can avoid overuse injuries associated with repetitive tasks.
Feedback Mechanisms:
Lay out channels for workmen to give feedback on ergonomic concern and ideas for improvement. Follow up on this feedback to improve ergonomics in the working environment continuously.
Ergonomic Appraisals:
Direct ergonomic evaluations of workstations to recognize and resolve possible issues before they lead to injuries or inconvenience.
Management Support:
Ensure that administration effectively upholds and advances ergonomics drives and designates assets for ergonomic enhancements.
Health and Safety Committees:
To jointly identify and address ergonomic issues, establish health and safety committees that include employees.
Key Components of Workplace Ergonomics
Let’s delve into the key elements of workplace ergonomics that fundamentally influence workmen well-being and efficiency:
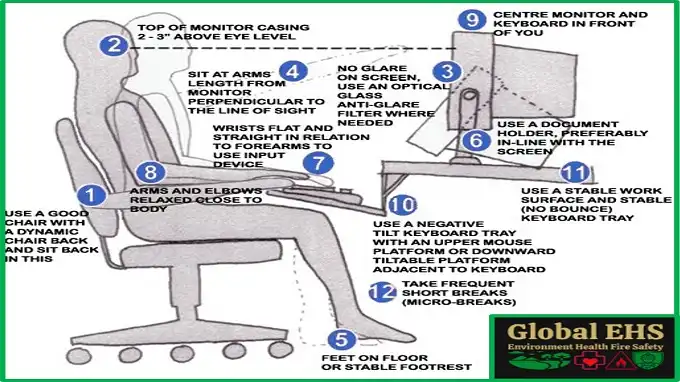
- Work area and Seat:
Choose chairs and desks that can be adjusted to fit people of all sizes and shapes. Seats support to offer lumbar help, and work areas support to consider proper keyboard and mouse placement. - Location of the Monitor:
Position screens at eye level to lessen neck strain. Utilize movable screen stands or mounts to accomplish the ideal level. - Keyboard and Mouse:
Put resources into ergonomic keyboards and mice that advance a natural wrist position. A keyboard tray can assist with keeping up with proper wrist arrangement. - Normal Breaks:
Urge workers to enjoy standard breaks to stretch and move around. This can prevent stiffness and improve circulation. - Lighting:
Guarantee proper lighting in the work area to decrease eye strain. Use task lighting to dispose of glare on screens. - Cable Management:
Keep links coordinated and far removed to prevent tripping risks and keep a perfect work area. - Ergonomic Accessories:
Provide ergonomic accessories like footrests, anti-fatigue mats, and document holders to enhance comfort and effectiveness.
Implementing Workplace Ergonomics
To harness the benefits of workplace ergonomics, consider the following steps:
- Assessment: Workstation ergonomic assessments can help you determine areas that need improvement. Encourage workers to report distress or pain.
- Training: Offer ergonomic preparation to workmen, showing them appropriate posture and how to change their work area for ideal comfort.
- Customization: Permit workmen to customize their work areas inside ergonomic rules. Perceive that everybody’s body is unique, and customization can further develop comfort.
- Feedback: Cultivate open communication among workers and management with respect to ergonomic concerns or ideas for improvement.
- Continuous Improvement: Consistently assess and adjust the work area to oblige changes in technology, tasks, or workmen necessities.
Bullet points summarizing the impact of workplace ergonomics:
- Workplace ergonomics enhances physical comfort and reduces discomfort.
- Improved comfort leads to increased employee focus and productivity.
- Ergonomics reduces the risk of musculoskeletal disorders and related absenteeism.
- Properly designed workspaces promote mental well-being, reducing stress and anxiety.
- Ergonomics fosters employee engagement and can contribute to higher retention rates.
- Cost savings result from fewer workplace injuries and workers’ compensation claims.
- Comfortable environments stimulate creativity and innovation.
- Ergonomics ensures compliance with labor laws and regulations, providing legal protection.
- Remote work necessitates considering ergonomics in home office setups.
- Ergonomics is often integrated into broader well-being programs.
- Sustainable design principles align with ergonomic furniture and accessories.
- A global approach to ergonomics caters to diverse employee needs.
- Integrating technology requires maintaining ergonomic principles.
- Continuous education and training keep ergonomic practices relevant and effective.